|
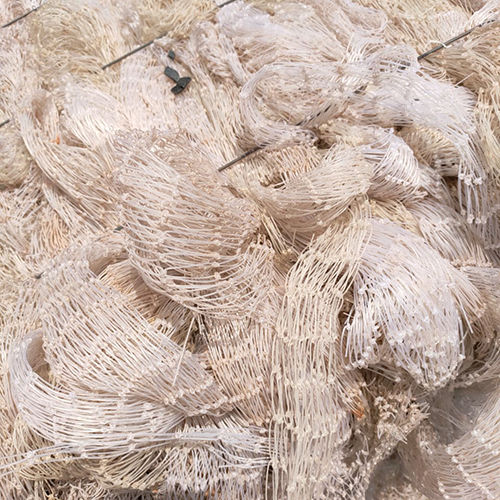
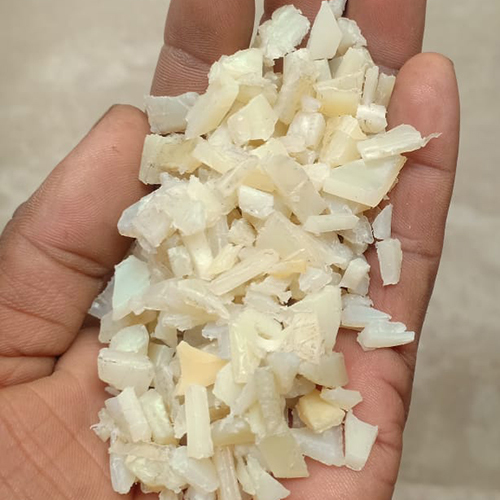
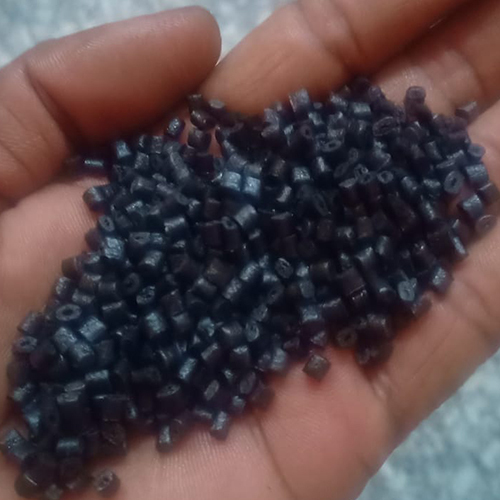
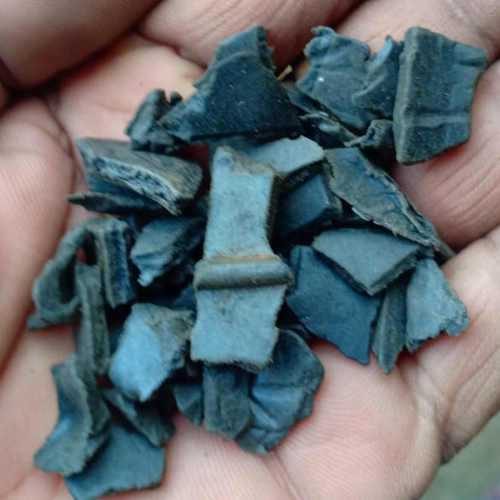
Waste Nylon Scrap
Product Details:
- Usage Industrial
- Type Mix Plastic Scrap
- Size Customized
- Click to View more
Waste Nylon Scrap Price And Quantity
- 100 Kilograms
- 180.0 INR/Kilograms
Waste Nylon Scrap Product Specifications
- Mix Plastic Scrap
- Industrial
- Customized
Waste Nylon Scrap Trade Information
- Cash Advance (CA), Cash in Advance (CID)
- 5000 Kilograms Per Month
- 10 Days
- Sample costs shipping and taxes has to be paid by the buyer
- as per customer requirement
- All India
Product Description
Waste nylon scrap refers to discarded or leftover nylon materials, often generated during manufacturing processes (pre-consumer waste) or from products that have reached the end of their useful life (post-consumer waste). It's a significant commodity in the recycling industry due to nylon's valuable properties and the growing demand for sustainable materials.
Here's a breakdown of its description:
What it is:
- Leftover material: This can include trimmings, spills, defective products from factories, or worn-out items like fishing nets, carpets, clothing, and even automotive parts.
- Various forms: Nylon scrap can come in different forms, such as fibers, fabric scraps, granules, rolled materials, or even larger pieces from industrial components.
- Source: It's primarily sourced from production facilities (post-industrial) and consumer products (post-consumer).
Key Properties of Nylon (and thus, its scrap):
Nylon, as a synthetic polymer, possesses several desirable characteristics that make its scrap valuable for recycling:
- Strength and Durability: Nylon is known for its high tensile strength and resistance to wear and tear, making it ideal for robust applications.
- Flexibility: It can be molded into various shapes and forms.
- Resistance: Nylon is resistant to abrasion, impact, chemicals, UV radiation, and moisture.
- Versatility: Its properties allow it to be used in a wide range of products.
- Non-biodegradable: This is a crucial property from an environmental perspective. Nylon does not decompose easily, taking 30-40 years to degrade, which highlights the importance of recycling.
- Melting Point: Nylon typically has a melting point between 190C and 350C, which is relevant for mechanical recycling processes.
Types of Waste Nylon Scrap:
Nylon scrap is often categorized by its type (the specific polyamide) and its source:
- Nylon 6 (PA6) and Nylon 66 (PA66): These are the most common types of nylon. Their scrap is widely sought after.
- Glass-filled Nylon: Some nylon materials are reinforced with glass fibers (e.g., PA66 GF30) for enhanced mechanical properties, and their scrap is also recycled.
- Post-Industrial Nylon Scrap: This originates from manufacturing processes, such as:
- Yarn waste
- Fabric trimmings
- Defective molded parts
- Airbag scraps (often a mix of PA66 and PET)
- Yarn waste
- Post-Consumer Nylon Scrap: This comes from end-of-life products, including:
- Fishing nets
- Carpets
- Textiles/clothing
- Automotive parts (e.g., engine components, interior panels)
- Nylon packaging
Uses of Recycled Nylon Scrap:
Recycled nylon scrap is a valuable secondary raw material used to produce a variety of new products, reducing the reliance on virgin materials and promoting a circular economy. Its applications include:
- Textiles and Fibers: New yarns, fabrics, and clothing (e.g., activewear, swimwear).
- Engineering Plastics: Automotive components (bumpers, airbag systems, fuel lines, engine parts), electronic housings, connectors, and cable ties.
- Consumer Goods: Office furniture, sporting goods, industrial components.
- Other Applications: Ropes, gears, injection-molded parts.
Recycling Process:
The recycling of nylon scrap typically involves several steps:
- Collection and Sorting: Gathering nylon waste from various sources and sorting it by type, color, and quality to ensure purity.
- Cleaning: Removing impurities like dirt, oils, labels, adhesives, and other non-nylon components.
- Shredding/Grinding: Breaking down the cleaned nylon into smaller pieces or flakes.
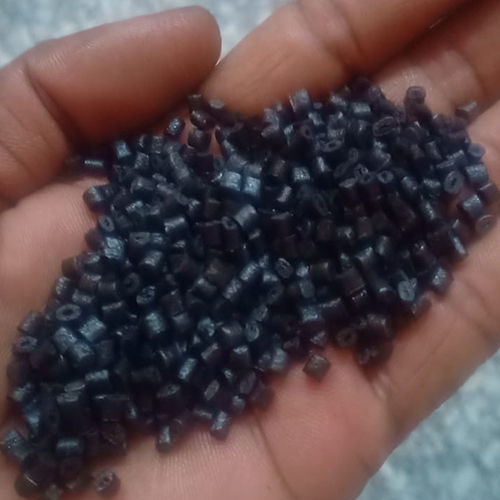
- Melting and Pelletizing (Mechanical Recycling): The shredded nylon is heated, melted, and extruded into uniform pellets (regrind or granules) which can then be used in manufacturing.
- Chemical Recycling (Depolymerization): A more advanced method where nylon is broken down into its original monomers (e.g., caprolactam for Nylon 6). These monomers can then be re-polymerized to create new nylon with virgin-like properties, often referred to as "closed-loop recycling."
- Compounding: Recycled nylon can be blended with virgin nylon or other additives and reinforcements to achieve specific properties for new products.
In summary, waste nylon scrap is a robust and versatile discarded material with significant potential for recycling, contributing to environmental sustainability by reducing waste, conserving resources, and lowering energy consumption compared to virgin nylon production

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Other Products in 'Nylon Scrap' category
 |
AB PLASTICS
All Rights Reserved.(Terms of Use) Developed and Managed by Infocom Network Private Limited. |